Pests are one of the main headaches for cannabis growers. There are many plagues that can affect our plants, so here are the most common, as well as different forms of treatment.
To prevent plants from being affected by any of these pests, prevention is the most important thing. If we have not managed to prevent the attack of any of these insects or mites, we must identify which is affecting us to control and eliminate it. Rapid action is very important to avoid the consequences that in certain cases can be irreversible.
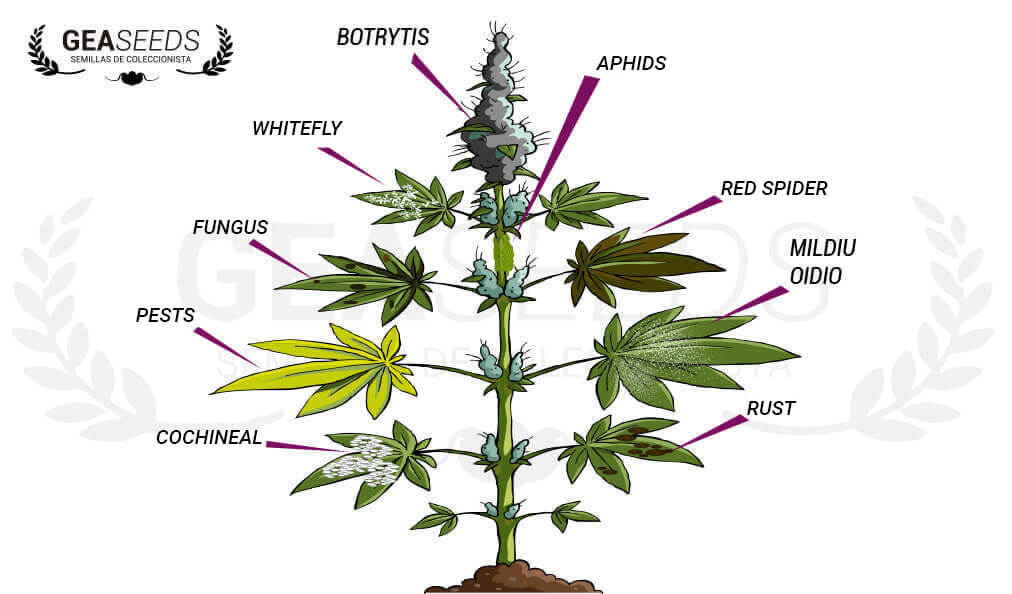
The most common marijuana diseases and pests that can affect cannabis are: insects, mites, fungi and viruses.
pests marijuana
- 1 Insects and mites most common in marijuana pests:
- 1.1 1. Whitefly:
- 1.2 Whitefly Treatment:
- 1.3 2.Red Spider:
- 1.4 Treatment against Red Spider:
- 1.5 3. Trips
- 1.6 Treatment for Trips:
- 1.7 4. The Aphid
- 1.8 Treatment against Aphid:
- 1.9 5. Leaf miner
- 1.10 Treatment for leaf miner:
- 1.11 6. Ground fly
- 1.12 Soil fly treatment:
- 1.13 7. The Caterpillars
- 1.14 Treatment against the caterpillars:
Insects and mites most common in marijuana pests:
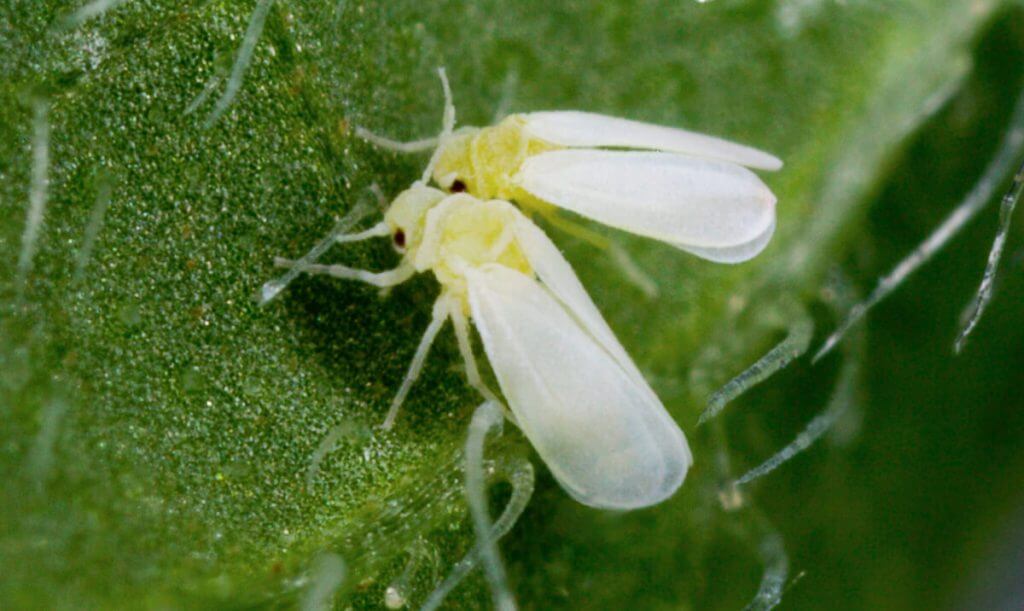
1. Whitefly:

Marijuana white fly
It is a poliphagus aleurodide insect, of which the species known as Bemisia Tabaci and Trialeurodes vaporariorum are mainly known. The whitefly is a small insect of approximately 2mm yellowish-white color.
It grows and reproduces very quickly. They are usually found on the underside of the leaf where they lay eggs and live larvae.
They feed on the plant by sucking the sap from the leaves, they can carry viruses and their droppings can also cause the fungus of the blush or boldface.
The direct damage they cause is derived from the suction of the sap that causes weakening of the plant and spots on the leaves (Chlorosis).
In addition, the whitefly can transmit different viruses and molasses from its droppings facilitates the appearance of the bold fungus.
Whitefly Treatment:
- Prevention: this pest can be prevented by using potassium soap or Neem oil or by growing other plants that repel this insect, such as basil or calendula.
- Biological control: biological control consists of introducing insects and parasites into our culture, predators of the plague that we want to combat. Predators of whitefly predators are the fly Encarsia formosa, Eretmocerus californicus, Macrolophus caliginosus or the fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus.
- Laying yellow adhesive strips
- Treatment with organic products such as rotenone or pyrethrins and in its absence can be used chemical products although this option is the least recommended and is convenient to use as a last resort and only when the other options have not worked.2.
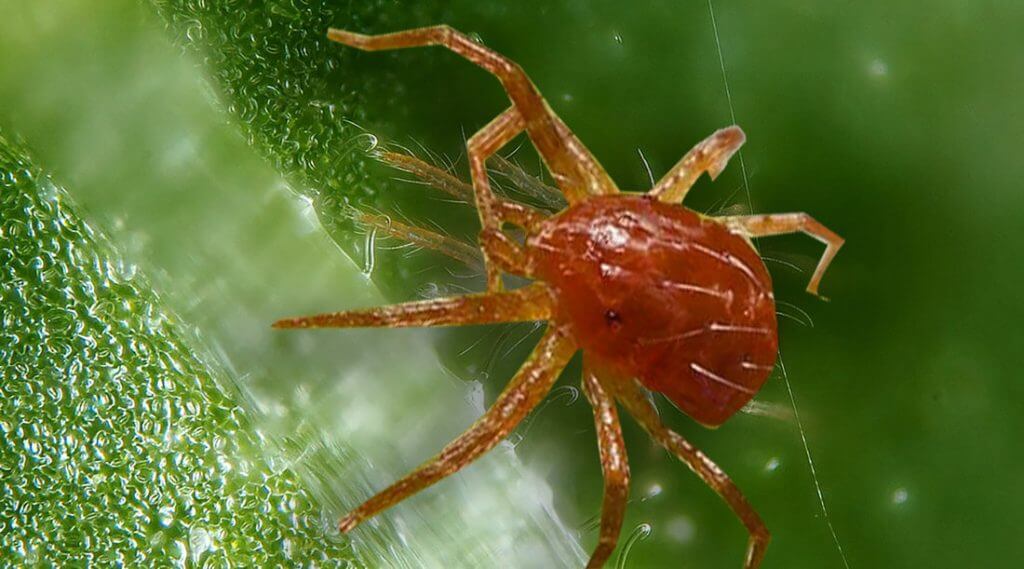
2.Red Spider:

Red spider
The red spider, known by the scientific name of Tetranychus urticae and Tetranychus cinnabarinus, is a mite that has become one of the most common pests in indoor crops and, if it is not treated in time, can have devastating consequences, even leading the plant to death.
It reproduces quickly in places with high temperatures, low humidity and poor ventilation.
The red spider feeds on the plant sap and lodges on the underside of the leaves. The first damages of this plague are manifested with the appearance of yellow points in the leaves, then the leaves yellowish and dry, in the most serious cases, their webs are found around the buds. This plague causes the general weakening of the plant and can lead to its death.
The red spider is very resistant because it reproduces very easily and is considered one of the worst plagues that exist.
Treatment against Red Spider:
- Prevention: maintaining high humidity during the vegetative period, temperature below 26ºC and avoiding fertilizers with a very high nitrogen content help to avoid this plague.
- Biological warfare: their natural enemies are phytoseiulus persimilis, neoseiulus californicus or Typhlodromus phialatus, among others.
- Acaricidal products can also be used, bearing in mind that these products act against the plague that we want to eliminate as well as against the rest of mites.
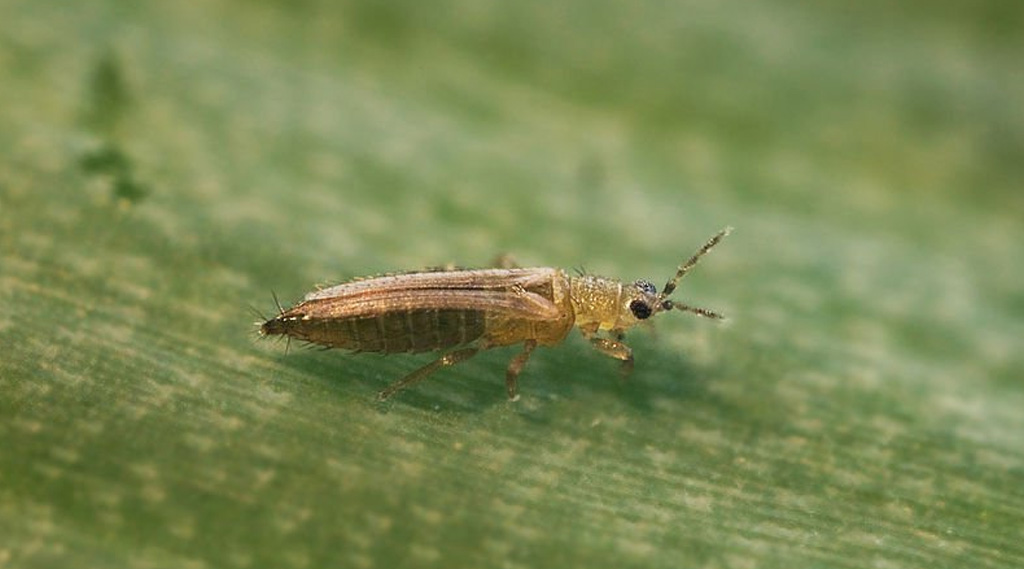
3. Trips

trips
Trip, specifically the species Frankliniella occidentalis, is an insect that constitutes one of the most common cannabis pests. The real problem caused by this pest derives from indirect damage caused by acting as a vector and transmitting diseases to the plant.
The trip is a small winged insect that feeds on the sap of the plant. It lodges in the underside of the leaves and inside the buds and warm temperatures favor its appearance.
The direct damage caused by trips is due to the leaves being sucked in to feed on the sap. The symptoms they cause are white and silver coloured spots on the leaves and even these can be deformed by their attacks and can cause serious damage by acting as vectors transmitting viruses.
This plague mainly affects indoor crops.
Treatment for Trips:
- Cultural control: placing blue adhesive traps will allow us to easily detect the presence of trips in our crop.
- Biological control: there are several predators of trips that we can use to eliminate them, such as the Amblyseius barkeri, Amblyseius cucumeris or the Amblyseius degeneraus.
- Phytosanitary: Products such as Neem oil can be used, which acts as a preventive and at the same time acts against this pest.
4. The Aphid
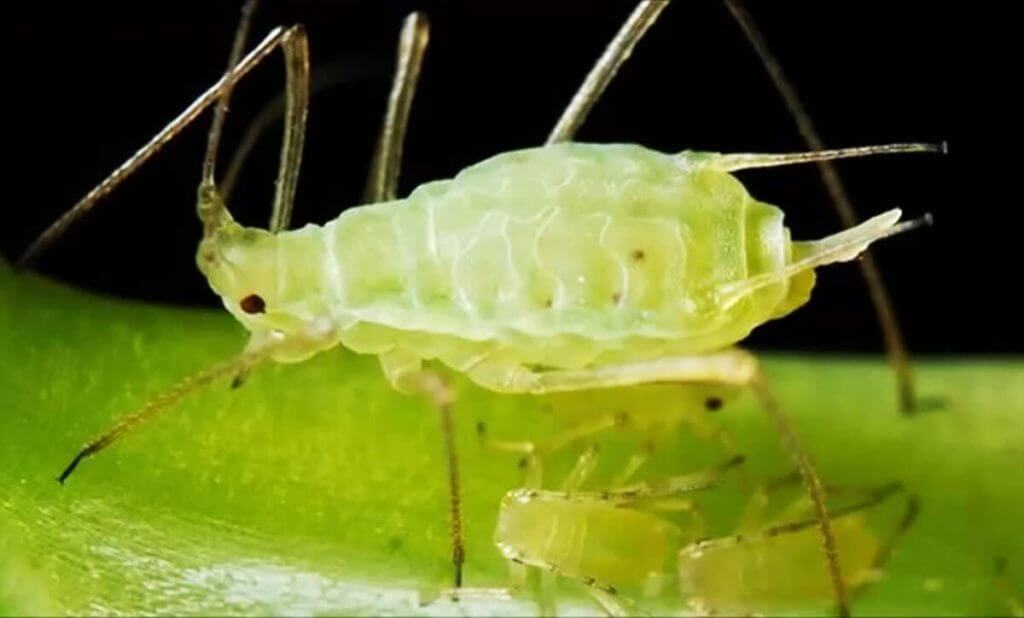

Aphid
The aphid is an aphid with a size between 1-10mm that can be of different colors (black, green or yellow). It is housed on the underside of the leaves and on the stem of the plant. It feeds on the sap which causes defoliation and yellowing of the leaves.
In addition, aphid can act as a vector transmitting viruses to plants and facilitates the appearance of fungi.
By reproducing quickly, they can invade the plant in a very short period of time.
Treatment against Aphid:
- Biological warfare: the predators of aphids are Coccinella septempunctata, Aphidoletes aphidimyza, Aphidius ervi, Aphidius colemani or Chrysoperla carnea, among others, which can destroy the entire aphid population.
5. Leaf miner
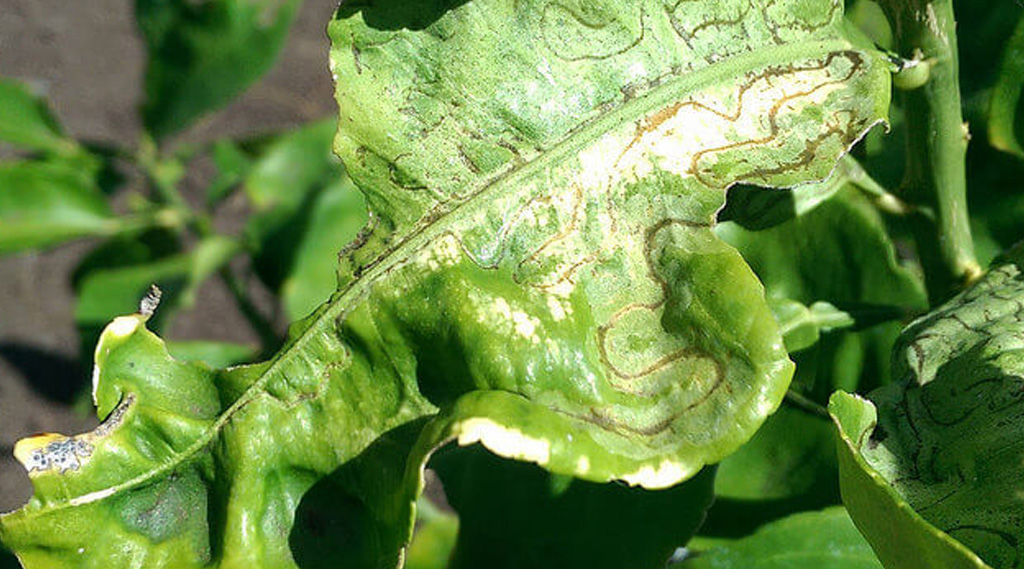

Damages caused by the leafminer insect
This small insect with the scientific name of Phyllocnistis citrella lives inside the leaves where it builds galleries which causes the destruction of the leaf. The eggs are deposited inside the young leaves and then the larvae are the ones that cause the damage.
Treatment for leaf miner:
- Prevention: it can be prevented by using Neem oil.
- Biological control: The natural predators of leaf miner are insects of the families Eulophidae, Braconidae, Encyrtidae and Elasmidae.
6. Ground fly
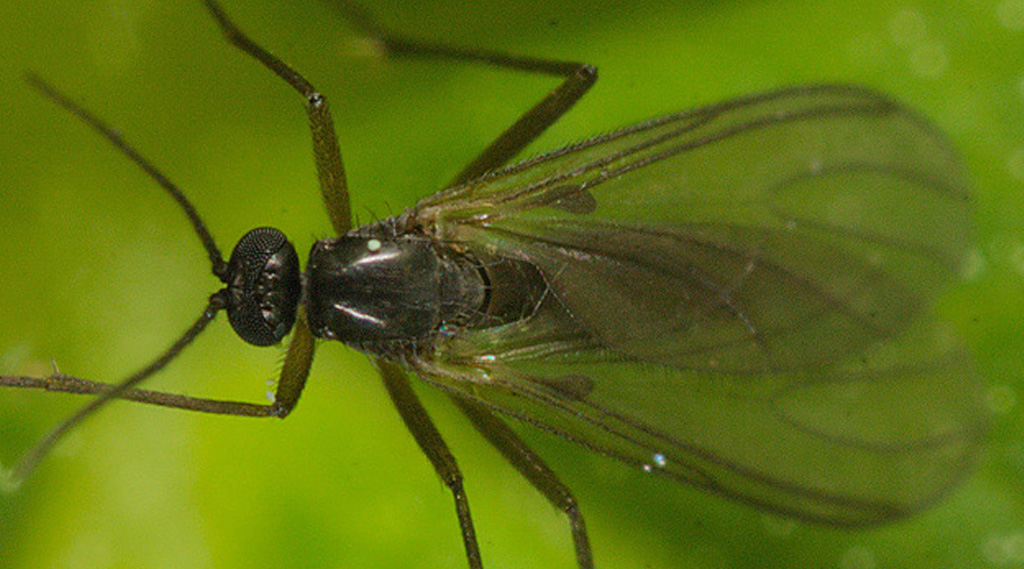

Ground fly
The soil fly or Sciaridae is a small dipterous insect that is usually housed in the substrate in indoor crops.
It is a small black fly whose larvae feed on root hairs, seriously affecting the root system of plants.
Their presence can be easily detected if small flies fly from the substrate as they move the pots.
They reproduce quickly in humid and dark environments and besides affecting the root system, they facilitate the appearance of fungi such as Fusarium or Botrytis.
Soil fly treatment:
- Prevention: using Neem oil will prevent the appearance of this pest in the plant.
- Biological control: The predators that feed on the soil fly are Atheta Coriaria, Hypoaspis miles or Steinernema feltiae, among others.
7. The Caterpillars
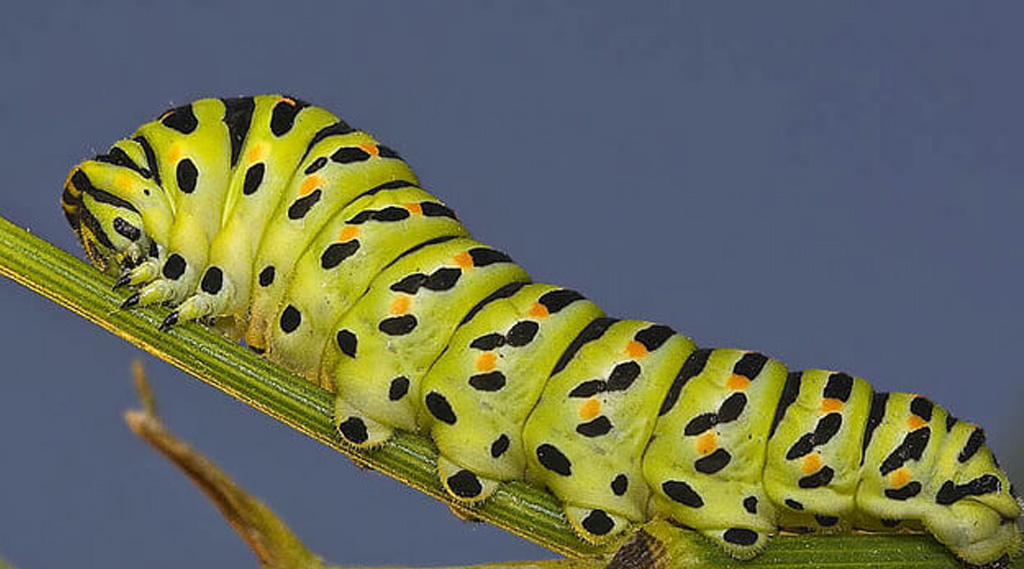

Caterpillars
The caterpillars, belonging to the family of lepidoptera, are a voracious plague that affects outdoor crops.
The butterflies and moths lay their eggs on the plants and larvae, then feed on the leaves and buds, devouring them and causing direct damage to the plants.
They have a predilection for plants during flowering, so their attacks favour the appearance of moulds and rotting.
Treatment against the caterpillars:
- Biological control: the natural caterpillar predators that we can use to combat this plague are Coccinella septempunctata or Orius spp., other parasites and pathogens can also be used to combat it.
- Biological products: one of the most effective products to control this pest is Baccilus thuringiensis, a bacterium that is marketed as a biological insecticide.
- Chemicals can also be used, but always as a last resort





guy mason
i have small very small like worms in the bud … is it a baby caterpillar will the same treatment work had plants near garden vegetable garden , moved to green house location , how can i get rid of them ?
Kare L
I have the same question I have been hand picking them.
Alex
“Tiny green worms” are Thrip Larvae
Spray them with insecticidal soap.