The intention of this article is to offer all kinds of information related to the diseases that affect the correct development of cannabis (as well as its causes and consequences). As every expert grower knows, diseases are many and fighting them takes a lot of time, dedication and effort. Below, we will summarize a wide and varied amount of information related to the types of diseases, the factors that favor their appearance and expansion, as well as the symptoms that provoke and help us to recognize them.

marijuana diseases
Introduction
Generally, losses in agricultural production are attributed to insect and parasite pests that attack crops. This is logical, as it usually is, but there is another factor that causes numerous losses in agriculture and yet it is not as well-known as the previous one; we are referring to what are known as plant diseases.
These types of diseases cause irreparable damage to crops, causing significant annual losses in agriculture. The following is a brief and concise summary of the various diseases that can affect our cannabis cultivation.
What is a plant disease?
Plant diseases are infectious agents and abiotic disorders that attack plants and negatively influence the development of their vital functions. This occurs when pathogenic microorganisms or environmental factors determine adverse changes in plant form, integrity or function, negatively affecting plant tissues and cells. The result is partial inability to perform their vital functions, and even death at worst.
How are marijuana diseases classified?
In terms of classification, it should be noted that they are divided into two main groups, parasitic and non-parasitic.
The former are those caused by microscopic organisms such as fungi, viruses, bacteria and nematodes, among others. On the other hand, non-parasitic diseases are those whose causative agents are not contagious and can be very varied. For example, non-parasitic diseases can be caused by adverse climatic conditions, as well as by excess or lack of irrigation, over-fertilization and, in general, poor agricultural practices.
It is estimated that approximately 10% of losses in the agricultural industry worldwide are caused by plant diseases. Therefore, this type of infectious agents and abiotic disorders are the cause of very important losses in agriculture. This gives us an idea of the importance of this type of disease, which, like the agricultural industry, also leads to numerous losses in cannabis cultivation.
marijuana diseases
Although being a very resistant plant species, marijuana is also affected by these diseases. In fact, it is estimated that there are approximately 100 plant diseases that directly affect the correct development of the vital functions of cannabis. This is the reason why we have decided to dedicate an entire article to the resolution of all types of doubts, providing the customer with the necessary information to know and prevent this problem.
Which parts of the plant are affected and how do they affect them?
Plant diseases do not attack plants in the same way. In fact, depending on the disease in question, the tissues and cells affected will be different and, therefore, the type of physiological function that will be affected will also be different. Below, we explain what parts of the plant affect infections and what functions they affect.
Firstly, to highlight the root infections, which can cause rotting of the same. If this happens, the plant will be unable to absorb the nutrients and water necessary for its proper development.
Secondly, diseases can also affect xylem vessels. For those less placed in the matter, it should be noted that xylem is the plant tissue formed by cells that carry the sap to the leaves. When xylem is affected by disease, the translocation of water and nutrients within the plant is negatively affected and vascular and fungal shriveling begins to appear.
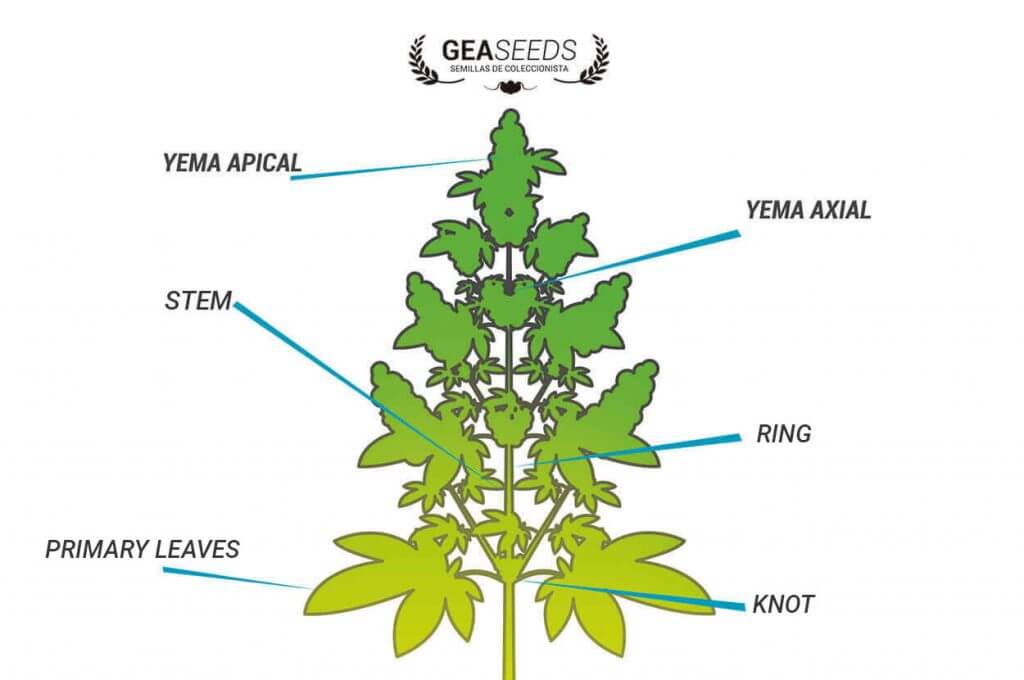
marijuana parts
Another part of the plant that is usually affected by plant diseases is the leaves. These infections directly interfere with the plant’s photosynthesis process and manifest themselves in the form of stains, rust, blight, mildew and mosaics.
Finally, it is worth mentioning the infections of flowers and fruits, which will directly interfere with the reproduction of the plant.
Most plant diseases cause infected plant cells to weaken or die. However, there are also other diseases in which infected cells are induced to divide more rapidly (hyperplasia) or to enlarge (hypertrophy) and thereby produce abnormal and amorphous tissues (tumors) or abnormal organs.
What diseases does marijuana get?
The following section reviews the main diseases that can affect the marijuana plant. These diseases are produced by microorganisms that attack the plant at a cellular level and subsequently destroy its tissues and organs.
Classification of cannabis parasitic diseases
The bacteria
When we talk about bacteria, we are referring to microscopic unicellular prokaryotes, that is, they do not have a defined cell nucleus (unlike fungi). Bacteria are very small in size, in fact, some are so small that they can’t even be seen with some optical microscopes. Phytopathogenic bacteria lack certain organelles and are therefore unable to meet their basic nutritional needs by having to parasitize other living or dead beings.
Bacteria marijuana
Viruses
Viruses are composed of sub-microscopic infectious entities, which in turn are composed of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) wrapped in a protein coating known as caspide.

Marijuana viruses
The mushrooms (Phytophagous fungi)
Phytophagous fungi are microscopic eukaryotic organisms, both unicellular and pluricellular. In addition, they all have cell walls, but lack photosynthetic pigments and their somatic structure is generally filamentous and branched.

Mushrooms
On the other hand, mention that these types of diseases can reproduce sexually or asexually. These organisms parasitize the cannabis plant and extract substances that are necessary for the strain to perform its life cycles. All this is because the lack of pigments forces fungi to make parasitism to survive.
The nematodes
Nematodes are a microscopically sized edge of vermes or pseudocelomate and semi-hyhaline-sized worms, also commonly known as round or cylindrical worms. These organisms are essentially aquatic, although they also proliferate in terrestrial environments and therefore their habitat is the water found in soil, plants and insects. There are free living nematodes, marine, soil and parasitic nematodes of plants and animals; the latter are the ones that we study and are known more specifically as phytoparasite nematodes.
The nematodes
In addition to these, there are other microorganisms such as viroids, mycoplasmas and protozoa, which also cause infections for cannabis.
The protozoa
Protozoa are microscopic and eukaryotic organisms, made up of a single cell or a colony of identical cells. In both cases there is no differentiation in the tissue and they live in aqueous media, either in salty or fresh water or in liquids from within a higher organism. These organisms appear mainly in humid environments; therefore, they are very frequent.
The protozoa
Nonparasitic cannabis diseases
After analysing the parasitic diseases of cannabis, we will focus on non-parasitic diseases that also affect this plant. In short, these types of diseases are caused by non-contagious causative agents such as agricultural malpractice. Some factors that can trigger these abiotic diseases include extreme levels of lighting, humidity, temperature, nutritional reactions and imbalances (both excess and deficiency), toxicity from pesticide excess, and weather-related damage.
Classification of non-parasitic cannabis diseases
The following list shows the most common non-parasitic diseases in cannabis cultivation, usually caused by agricultural malpractice.
Over and under irrigation
For diseases caused by agricultural malpractice, excess and poor irrigation are two of the most common problems. Obviously, cannabis plants need water to ensure their hydration, nutrition and therefore their proper development. For indoor crops, it is vitally important that irrigation is designed to provide the plants with the necessary water. If the plants do not receive the necessary water, they will be dehydrated, and we will spoil our harvest, as if we exceed the amount of water we add to our crop. Excessive watering can result in excessive moisture that rots the roots and causes fungus and mold to appear; we can also leave the soil without oxygen. It is necessary to control irrigation if we want good results.

Excess and deficiency of irrigation
But these two practices also cause multiple complications in our harvest and, in the worst case, the death.
Deficiencies and toxicities
Another of the most common abiotic diseases is usually nutritional deficiency or toxicity, the triggers of which can vary widely. Therefore, we must be aware of the amount of fertilizer that we administer to our plants, otherwise, if we go too far, we can kill the plants by overfertilization. This does not mean that we should not give plants certain dietary inputs. It should be borne in mind that if the crop does not have the necessary nutrients, the biological processes will be paralysed and the harvest spoiled. In short, the correct use of vitamins and nutrients consumed by our plants is of vital importance for their optimal development.
The “Sunshine Stroke”
This disease occurs when the crop is exposed to high temperatures and does not have enough water available for transpiration; therefore, plants are unable to cool the leaf surface. When this happens, burns appear in the larger leaflets, these being delimited by the main veins. Generally, the varieties of the indica subspecies tend to be more affected by sunstrokes, while plants with Sativa predominance tend to resist them better. To avoid this disease, we must make sure that the plant always has the necessary water and, if this is not possible, that it is under an area where there is no excessive sunshine.
pH and EC misalignment
Finally, to mention another disease that usually affects marijuana plants, the “orange spotted”. This non-parasitic disease occurs when there is a mismatch in the pH and EC levels in the culture medium. These imbalances in the acidity parameters of the water cause severe burns to the root system.
Once the misalignment of these parameters begins, orange-oxide necrotic spots begin to appear on the leaves and then the leaflets are necrotized. At first it is the older leaves that begin to suffer the appearance of these points, but then begin to appear also in the newer ones. Once this happens, production losses are inevitable.
What factors influence the occurrence of plant diseases in cannabis?
The following is a classification of the main factors influencing the occurrence of plant diseases in cannabis. Firstly, the factors that cause parasitic diseases are analysed, and secondly, the factors that cause non-parasitic diseases.
Factors influencing the occurrence of parasitic diseases
1. Disease stockpiles
This factor depends directly on the geographical area in which the crop is located. In Spain, diseases such as grey mould and powdery mildew are common, both indoors and outdoors.
2. Climatic conditions
Another factor closely related to the first one, is climatic conditions, a basic factor for the development of diseases. When temperatures in a crop are pleasant and humidity levels are high, the conditions are ideal for the appearance of biotic diseases.
3. The cultivated strain
Cannabis is a plant from which hundreds of hybrid strains have been produced. Obviously, they all have different biological behaviors and are affected differently by diseases. There are strains that are generally much more resistant than others. Some strains are more resistant to fungi and general moisture problems. Others, however, are better able to withstand drought, cold or lack of nutrients. Therefore, to know which factors we should pay more attention to, we must be well informed about the strain we choose and its specific metabolic behavior.
4. The feeding
Marijuana plants works better with fertilizers and nutrient complexes that stimulate and enhace their growth and flowering. There are a lot of studies that confirm and conclude that a down-nitrogen diet makes plants more resistant.
| Disease Spread | Disease Spread |
| Mushrooms | Rain, wind, irrigation water, insects, mites, mites, nematodes, soil, substrates, seeds, clones, man |
| Bacteria | Rain, irrigation water, wind, insects, mites, mites, seeds, nematodes, clones, people |
| Viruses | Insects, mites, nematodes, seeds, clones, elastic people |
| Nematodes | Rain, wind, irrigation water, soil and substrates, clones, people |
| Protozoa | Rain, wind, water, land |
Parasitic diseases table
What are the most common means of propagation?
Any parasitic disease requires a means by which it can be transported to the subject it will parasite. The means used by diseases are many and varied, from a little soil, water, a seed, an infested host or the wind. Below is a list of the various media, also called vectors.
Factors influencing the occurrence of non-parasitic diseases
As the name suggests, non-parasitic diseases have nothing to do with parasites. These diseases are related to some of the factors listed above, such as climatic conditions, crop variety and diet.
Visual symptoms of diseases
The main problem to recognize which disease is attacking our crop is to be able to relate the symptomatology with the problem that produces it. There are some diseases that we can easily recognize by their symptoms, such as powdery mildew on leaves or grey mould on flower tops. But unfortunately, many other symptoms can lead us to confuse a parasitic disease with one that is not. For example, a root apoxy (a very typical non-parasitic disease) can be confused with Fusariosis, a nematode root attack (macroscopic symptoms are very similar), or a magnesium deficiency.
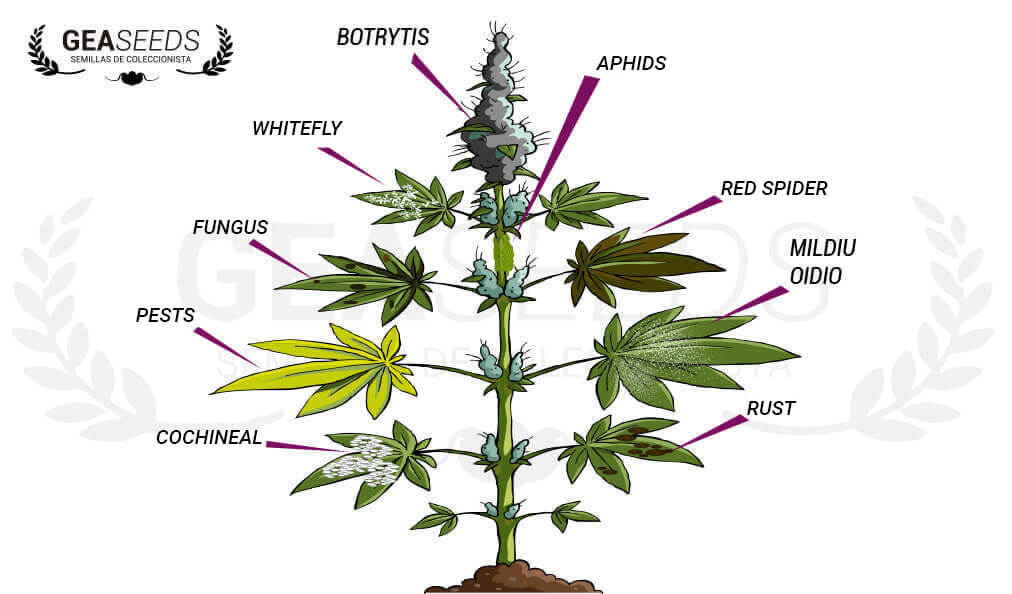
Marijuana diseases
In many cases, the symptoms of different diseases are similar, but their causes and therefore their solution are not. This means that we must be extremely careful when applying the corresponding remedy, otherwise we could be applying a treatment that does not correspond to the needs of our crop.
Terms related to the visual symptomatology of plant diseases
Below, we show you the most common ways to name the various symptoms that usually appear in marijuana plantations.
Visual symptoms
1. Necrosis
Necrosis is the degeneration of tissue by cell death. The visible symptoms on plants are dark spots on leaves and other plant organs. Necrosis can be located in specific tissues or spread to entire organs.
Necrosis is caused by fungi, viruses, bacteria, nutritional disorders or irrigation. As noted above, adverse environmental conditions such as excessive low or high temperatures can also cause necrosis.
2. Marchitez
Another factor that we wanted to highlight in the second place is wilting. This symptomatology is directly related to the water deficit. If there is not enough water in the plant to maintain tissue turgor, the plant withers. This phenomenon can be caused by lack of water or root damage, either by an infectious agent or by another abiotic one.
3. Chlorosis
Chlorosis is yellowing that occurs in the green parts of plants, usually on the leaves and due to the lack of activity of their chlorine plastos. This yellowing may be nerve or inter-nerval, and its symptoms are closely related to infections with bacteria, fungi, viruses, and nutritional disorders.
4. Color changes
When a plant undergoes color changes it is usually related to infections caused by parasitic agents, but also by changes in environmental and nutritional conditions.
5. Abnormal growth
Sometimes plants suffer abnormal changes in growth. This can be caused by both parasitic and non-parasitic diseases. For example, poor lighting or low temperatures can slow plant growth. On the other hand, strains that have been over-fertilized or affected by fungi are also negatively affected growth.
These have been some of the most common visual symptoms of marijuana plants. However, there are many other symptoms such as atrophy, hypertrophy, hypoplasia and hyperplasia. Atrophy is a decrease in the volume or size of an organ or organic tissue due to physiological or pathological factors.
While hypoplasia consists in the incomplete or stopped development of an organ or part of it. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia are the opposite of both concepts respectively.
This has been a synthesis of everything related to plant diseases, from their significance and classification to the factors that influence their appearance and symptoms. If you still have any questions after reading it, please contact our website or telephone service and we will solve them. In addition, you will be helping us to further complete this article and make it more useful to the next reader.








ANTHONY DEBBARMA . C/O.
Love it so much ✌️✌️✌️✌️