THC, also known as tetrahydrocannabinol or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (9-THC) is, together with CBD, the main active compound of cannabis, being responsible for its psychotropic properties. The idea of the following article is to synthesize all the necessary information about THC, its composition, its effects, its benefits, the different ways of consuming it, as well as a wide variety of factors related to it.

THC
How does THC affect us?
THC works as a palliative, relieving pain. In addition, depending on the type of marijuana and THC levels, it can also produce euphoria, stimulating our brain thanks to the release of dopamine. Dopamine is a brain neurotransmitter that directly affects the motor functions of our body.
Another way in which THC affects our organism is to process thoughts, memories and in general, mental processes. This characteristic affects our behavior and can lead to mental health problems, triggering some symptoms of schizophrenia.
On the other hand, it also affects the digestive system, stimulating the appetite or suppressing it, depending on the person, time and amount consumed. Therefore it is increasingly being used to treat diseases related to the digestive system or simply cause nervousness, nausea or vomiting.
Why does THC affect the brain?
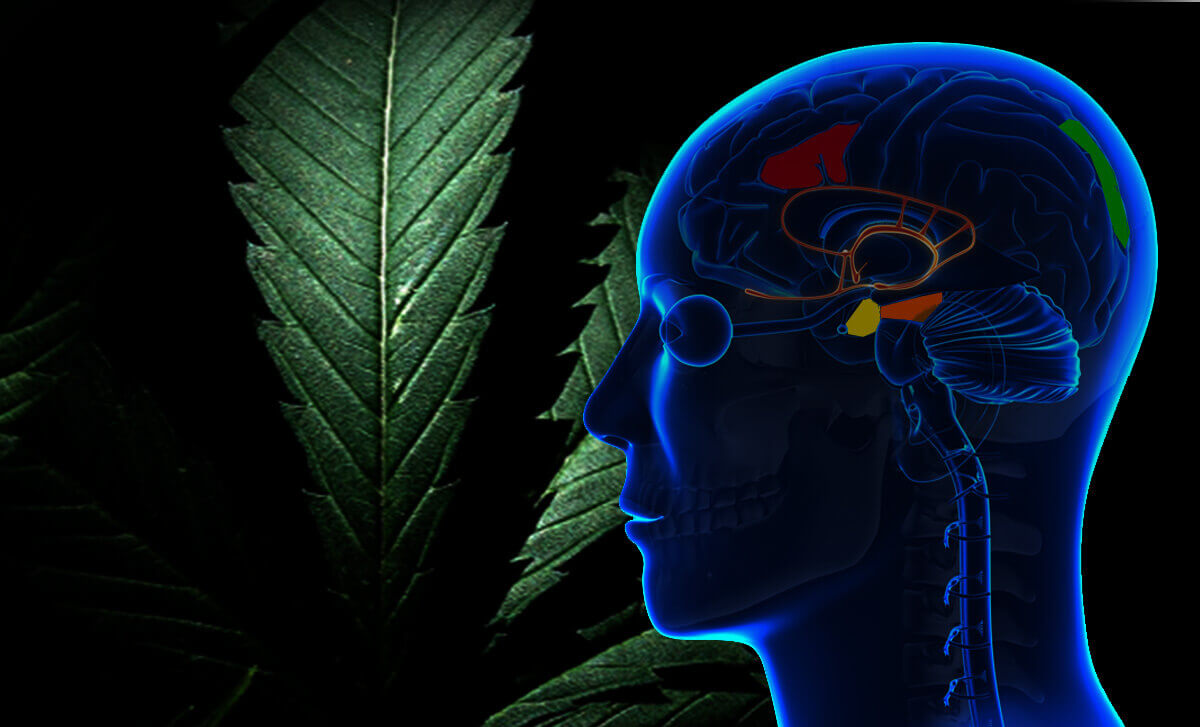
THC is the main psychoactive constituent of cannabis and affects our brain activity due to its direct connection with nerve cell receptors. The cannabinoid receptors are directly related to motor coordination, memory, pleasure, thought, balance or the perception of time, among many other things. When we use cannabis, and therefore THC, we are making changes in nerve cell receptors, affecting brain activity and more specifically the functions we have previously mentioned. In short, the human brain has different densities of receptors, depending on the area of the brain, and as THC adheres to cannabinoid receptors in our body, it produces various effects.
What are cannabinoid receptors and how do they work?
Cannabinoid receptors are receptors of cell membranes, coupled with G proteins. Understanding what exactly the cannabinoid receptors are is complicated without minimal biological knowledge, but it is easier to understand if we understand how they work. First, it should be noted that nerve cells communicate by passing chemical signals through synapses, which are points of contact between them. On the other hand, THC adheres to these receptors, modifying connections and, therefore, nerve activity. In other words, it is as if THC affects the messenger between cells, and as it affects connections, it also affects the result.
List of THC body receptors and effects
RECEIVERS (FUNCTION CONTROLLING) | EFFECTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where is THC located?
THC is found in resin glands of female marijuana plants. In fact, it is located in the reproductive organs, specifically the buds. When the THC dries up, it undergoes a chemical transformation that makes it acquire the psychological and physical effects that made this plant so famous.
The THC levels in the plant depend on a wide variety of factors such as temperature, humidity, plant nutrition, strain and, in general, all related factors are its aging. Therefore there are varieties whose THC levels are so low that they are not considered marijuana but hemp and are therefore legal. In fact, marijuana is a type of hemp that has been crossed and selected to enhance the concentration of THC or tetrahydrocannabinol, accentuating its psychoactive effects.
It should also be considered that THC is not the only active compound in cannabis; cannabinoids are many and varied, at least nine and some of them, such as CBD, counteract THC.
Other active cannabis compounds
It should be noted that there are also other active compounds in weed such as:
- Cannabinol (CBN): is a psychotropic cannabinoid located in Cannabis sativa and Indian/Afghanic Cannabis. This metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) performs the function of weak agonist in the CB1 and CB2 receptors, but with less affinity than THC.
- Cannabigerol (CBG): non-psychoactive cannabinoid located in marijuana. This active ingredient is more concentrated in hemp, while cannabis strains grown for consumption contain less of it.
- Cannabicyclol (CBL): non-psychoactive cannabinoid of cannabis. CBL is degrading, as is canabinol, as light converts cannabicromene into CBL.
- Cannabicromene (CBC): abundant natural phyto-cannabinoid and is believed to be the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana plants. It produces antinociceptive (analgesic) and anti-inflammatory effects, increasing the interest in its future medicinal potential as a palliative treatment for inflammatory and gastrointestinal disorders
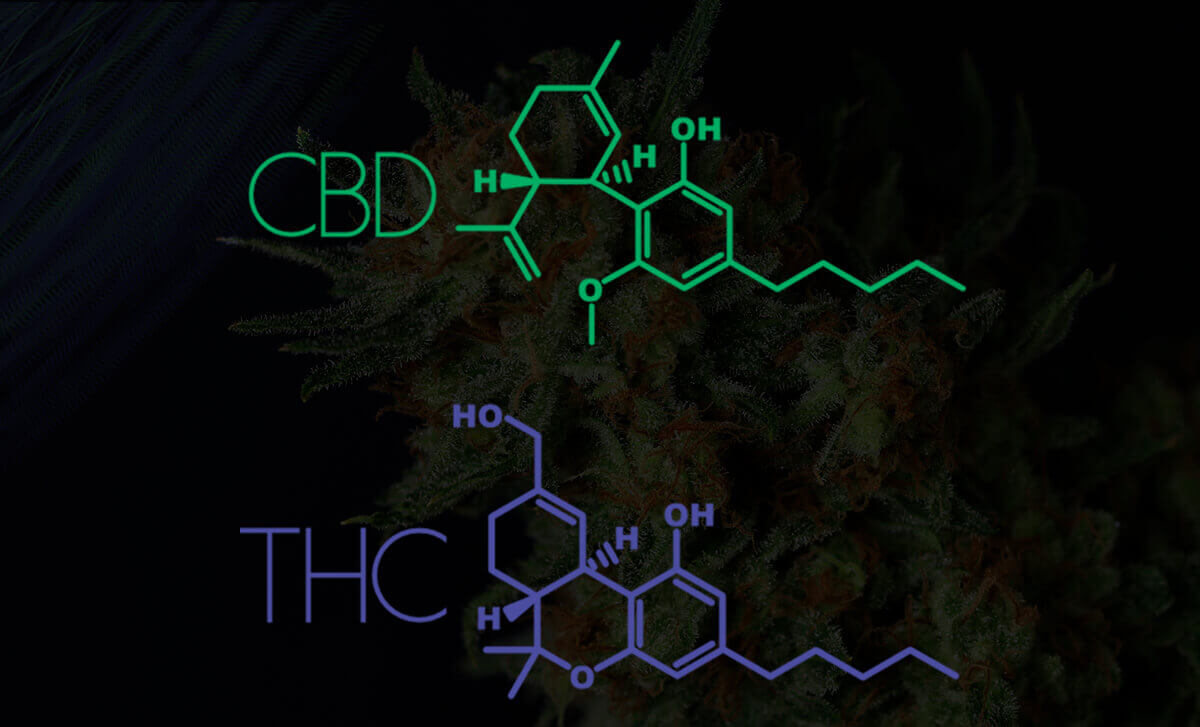
THC and CBD
CBD Vs THC
These two acronyms represent the two main active compounds of cannabis. In fact, THC produces the psychoactive effects of marijuana, while CBD is responsible for the medicinal effects. This is because when CBD interacts with cannabinoid receptors, it stimulates and activates natural responses in the nervous system that reduce feelings of anxiety, pain, inflammation or stress. In addition, these two compounds work individually against cancer and when they work together they generate synergy. The concrete results of this synergy have yet to be further investigated.
Is today’s cannabis much higher in potency?
In summary, it should be noted that THC is the main psychoactive substance of cannabis, and, is therefore the most abundant in the varieties of marijuana grown for human consumption. In fact, as noted above, varieties are now crossing and trying to reach maximum THC levels, obtaining psychoactive effects that are increasingly potent. In fact, many varieties now contain between 10% and 20% THC, which is in stark contrast to the low levels of THC found in marijuana plants consumed just 15 or 20 years ago.








