Aquaponics is a closed technique or growing system, based on aquaculture and hydroponic growing. The origins of this technique are blurred, due to scarce background knowledge; regarding vague scientific agreement, the most notorious hypotheses locate its origin in Mesoamerica – Aztec Empire, China or Thailand. Next, we are solving some doubts related to this magnificent symbiosis between marijuana growing and fish farming.
The word has an English origin, and its etymological roots lay on two terms of English language: ‘aquaculture’ and ‘hydroponics’; another term is used for this technique: aquapony, from the words ‘aquaculture’ and ‘hydropony’.
Involved organisms
Working on an aquapony growing, three different living organisms are necessary: fish, plants and nitrified bacteria. The plants eat fish excrements, processed by nitrified bacteria, so these bacteria have a very important role, being responsible of biofiltration – process which transforms the toxic wastes of the fish into nitrogenous nitrate, main plant food; besides, plants purify water, providing a healthy, clean mean, so fish can live.
Just one doubt: how do nitrified bacteria get fed? Very simple; they obtain the energy thanks to the oxidation of nitrogen inorganic compounds.
What is aquapony and how does it work?
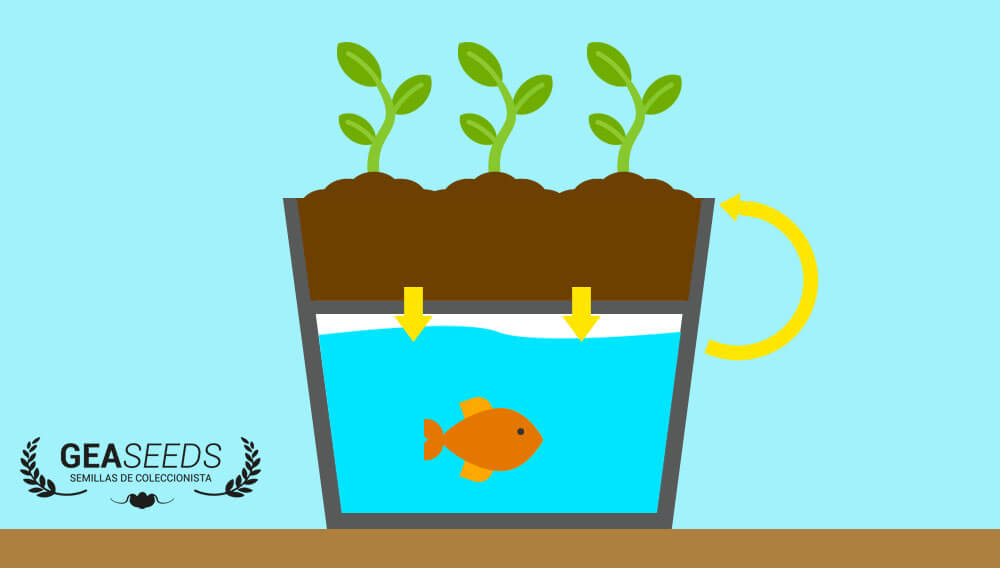
Aquapony is a growing system, focused on water, which combines plant growing and fish farming without any solid substrate; the method is considered as a sustainable production system, because breeding fish and plants benefit the symbiotic exchange.
For this symbiosis, breeding fish, shrimp or crab excrements are accumulated in the water, and the plants are fed by this water, working as a subsystem.

The chemical explanation is kind of complex: breeding fish and animal excrements are decomposed and transformed into nitrites, and, then, into nitrates, thanks to nitrification bacteria; next, plant roots, grown by hydroponics, will suck those nitrates, and will assimilate them as nutrients. Following up, a part of the water will come back to aquaculture subsystem, so it could be considered as a recirculation system; being fed by the metabolites of the nitrified fish wastes, the plants remove the water toxicity, that is, the water is treated naturally, so fish keep on living in it perfectly.
Summing up, fish food becomes plant food, because fish excrements provide all the necessary nutrients for the proper development of the vines, and, the plants, being fed by the excrements, clean up the water, so fish keep on living in it.
Advantages
A symbiotic system, like aquaponics, has numerous advantages, for the environment and the grower; about the environment, aquaponic growing reduces runoff, leaching and wastewater dumping: besides, when reducing the wastewater and mineral dumping, subterranean water is less contaminated; less wasted water, and better sustainability.

Grower’s advantages are obvious; less water expenditure: it is recycled, and it is used for two things; less plant nutrients, because the fish produce that food. Besides, the plants clean the water, so you will not have to worry about changing it and about controlling its toxicity levels; a much cheaper way of plant growing and fish farming, with less effort.
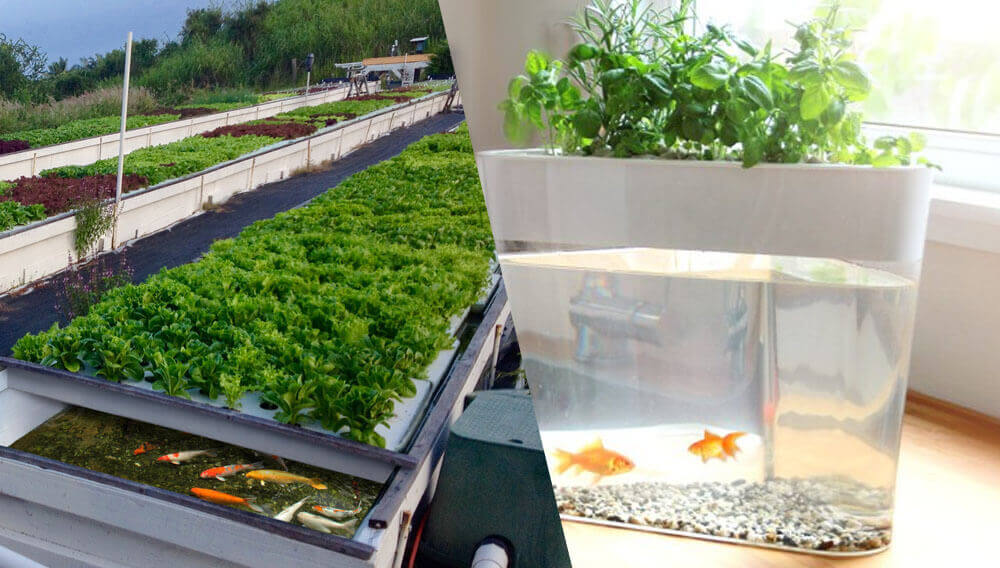
Sizes and types
Regarding the size of aquaponic growings, there is not any standard size; aquaponics is performed from indoor small unities to huge business units. Similarly, it is an outdoor technique, with freshwater or salt water, depending on the type of fish farming, and the type of growing plants.
As a conclusion, aquaponics can be performed by several ways, but the symbiotic functioning is always the same; anyway, it is currently in process and, undoubtedly, it will notoriously improve in a few years.



